2.2. Python installation#
In this course, we will use Python 3.12.2 because we want to utilize an autograder in Jupyter Notebook to provide you with instant feedback on your answers to some of the questions. It is very common for an OS, Windows or otherwise, to have multiple Python installations, so you may install different versions of Python on your computer. Python 3.13, for example, allows you to exit the Python shell using exit instead of exit(), which you may prefer when working on other projects.
2.2.1. Check Python Version#
Let us check what version(s) of Python are installed in your computer already.
Windows does not ship with a Python version by default. However, since Python is widely used, your computer may already have some versions of Python installed. You use the Windows Python Launcher (py.exe) in PowerShell and the where python command at the Command Prompt (cmd.exe) to see the current Python installation(s) (here I have a version 3.12 installed already).
With Windows PowerShell, where python does not give us anything, but the py launcher shows all installations and the default Python:
PS C:\Users\[user]> where python
PS C:\Users\[user]> py -0
-V:3.13 Python 3.13 (64-bit)
-V:3.13-arm64 Python 3.13 (Store)
-V:3.12 Python 3.12 (64-bit)
-V:3.10 * Python 3.10 (64-bit)
PS C:\Users\[user]>
With Command Prompt, the py launcher gives us the same information, and where python gives us the paths of the Python executives.
C:\Users\[user]>py -0
-V:3.13 Python 3.13 (64-bit)
-V:3.13-arm64 Python 3.13 (Store)
-V:3.12 Python 3.12 (64-bit)
-V:3.10 * Python 3.10 (64-bit)
C:\Users\[user]>where python
C:\Users\[user]\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python312\python.exe
C:\Users\[user]\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python313\python.exe
C:\Users\[user]\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python310\python.exe
C:\Users\[user]\AppData\Local\Microsoft\WindowsApps\python.exe
C:\Users\[user]>
If you are using macOS, you already have a version of Python shipped with the OS. You may issue the following commands in the command line (using Terminal.app) to see the version(s) of Python you have in the current system. In most cases, you may need to use python3 instead of python. Also, which python3 will give you the path of the Python executable.
[user]@[host]:~/workspace/dsm$ python3 --version
Python 3.12.2
[user]@[host]:~/workspace/dsm$ which python3
/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.12/bin/python3
[user]@[host]:~/workspace/dsm$
2.2.2. Install Python#
If the check above does not yield any results, or if you don’t see Python 3.12.2, go to python.org and download the installer of the specific version and install it. If you are on macOS, after installation, check to see if the intended version is installed using python2 or python.
$ python3
Python 3.12.10 (main, May 22 2025, 21:57:53) [Clang 14.0.0 (clang-1400.0.29.202)] on darwin
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>>
If you are a Windows user, the situation is somewhat more complex. When you search for Python from the Windows search bar, by default, it will bring you to the Windows Store for the current version of Python. However, the path of the Python installed will not be added to the PATH environment variable. It is therefore recommended to download the Python installer from python.org for installation.
If you installed Python through the Windows Store, the installation runs automatically. You can check this installation using where python in Command Prompt, and you will see that a python.exe is in the C:\Users\[user]\AppData\Local\Microsoft\WindowsApps\ directory:
C:\Users\[user]> where python
C:\Users\[user]\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python312\python.exe ### python.org installer installation
C:\Users\[user]\AppData\Local\Microsoft\WindowsApps\python.exe ### Windows Store installation
We can check the newly installed Python version by going into the location and running the Python executable to see the version.
cd \Users\[user]\AppData\Local\Microsoft\WindowsApps
C:\Users\[user]\AppData\Local\Microsoft\WindowsApps>.\python.exe
Python 3.13.7 (tags/v3.13.7:bcee1c3, Aug 14 2025, 14:15:11) [MSC v.1944 64 bit (AMD64)] on win32
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>>
Since Python 3.12.2 is an earlier version, installing it by downloading the Python installer from python.org is preferred. Simply navigate to the download section of the site, search for the desired version, download the installer, and double-click it to initiate the installation. Make sure that you check the options below when installing:
Use admin privileges when installing py.exe (this enables py.exe to manage all Python installations)
Add python.exe to the PATH environment variable (this sets this installation as the default Python)
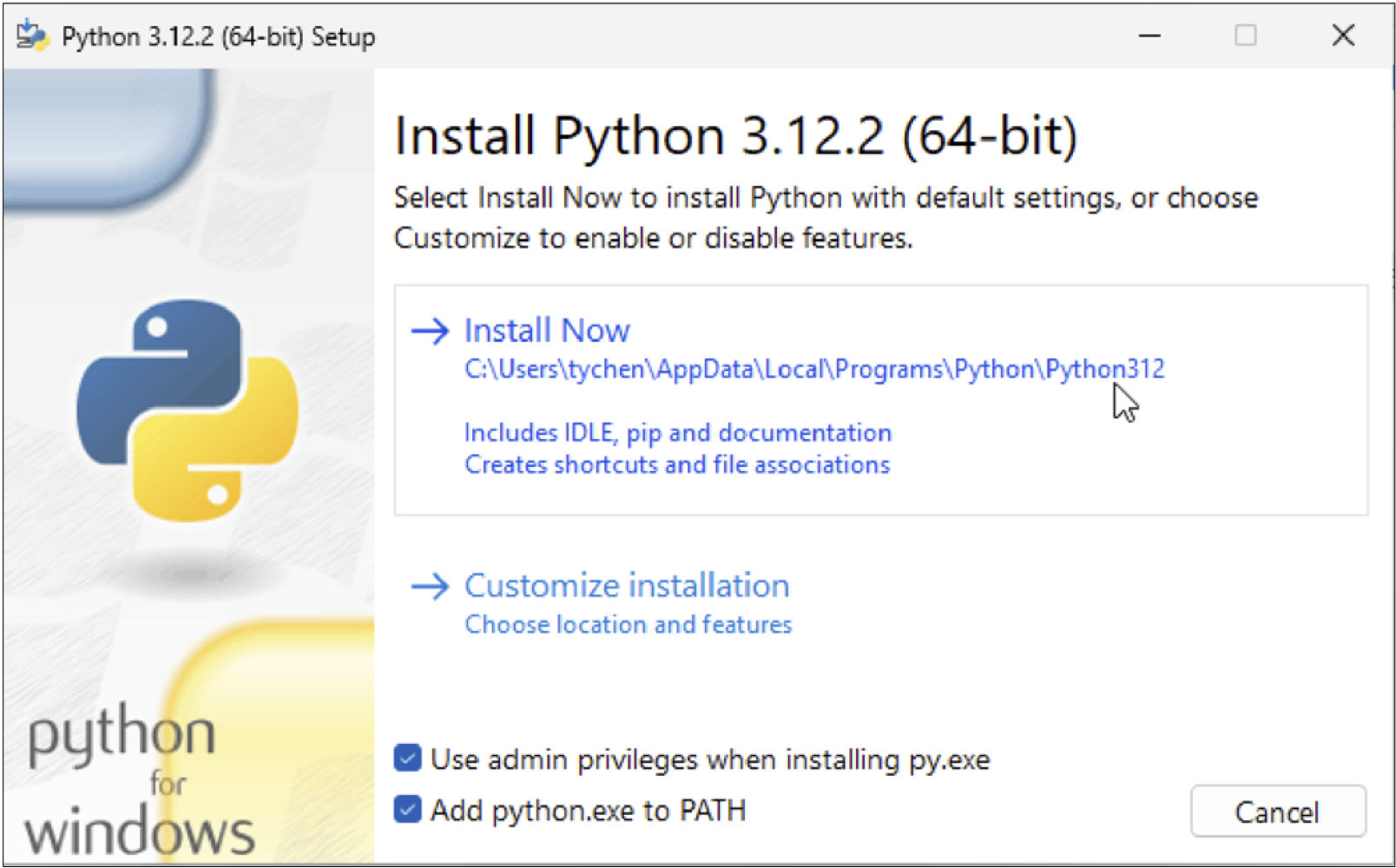
Fig. 2.4 Python Installation Options in Windows#
After completing the installations, you may check the Python installations you have using Windows PowerShell:
PS C:\Users\[user]> py -0
-V:3.13 * Python 3.13 (64-bit) ### if you use py launcher this is the default Python
-V:3.13-arm64 Python 3.13 (Store)
-V:3.12 Python 3.12 (64-bit)
PS C:\Users\[user]>
In Windows Command Prompt, you may see:
C:\Users\[user]>where python
C:\Users\[user]\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python313\python.exe
C:\Users\[user]\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python312\python.exe
C:\Users\[user]\AppData\Local\Microsoft\WindowsApps\python.exe
2.2.3. Choose Python Version#
2.2.3.1. Choose Python version temporarily#
In case you have more than one Python version installed, you may need to control the version of Python that you use for your projects. If the default Python is different from the desired version, you may use the version suffixes to designate the desired Python version. This helps, e.g., when you need to create a virtual environment and you need to designate a Python version such as 3.12.
In Windows, you may use the Python launcher to decide which Python version to use. This means, instead of issuing the python command, you use py -Major.Minor to control which Python version to use. For example, to use version 3.12, we issue:
C:\Users\[user]>py -3.12
Python 3.12.2 (tags/v3.12.2:6abddd9, Feb 6 2024, 21:26:36)
[MSC v.1937 64 bit (AMD64)] on win32
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>>
In macOS, we append the Python version number in the format of Major.Minor when issuing python to choose the Python version to use:
$ python3.12
Python 3.12.2 (v3.12.2:6abddd9f6a, Feb 6 2024, 17:02:06)
[Clang 13.0.0 (clang-1300.0.29.30)] on darwin
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>>
2.2.3.2. Set Default Python Version#
You can also change the system default Python version for the command python by modifying the path entries in the operating system’s PATH environment variable (restarting the computer may be needed).
In Windows, you want to move the desired Python entry to the top of the PATH environment variable:
Press Start and search for “Environment Variables”.
Click “Edit the system environment variables”.
Click on the “Environment Variables” button at the bottom of the window.
Under System variables, find “Path” and click to highlight it.
Click Edit
Move the folder for the version you want to the top of the list
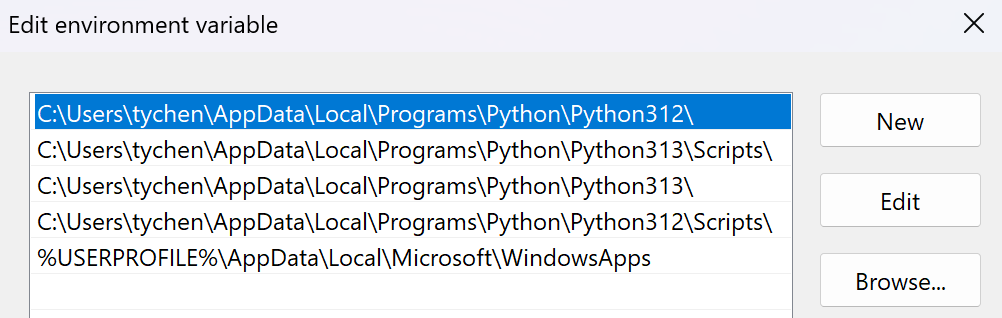
Fig. 2.5 The top Python path is the default Python#
This will point python to your desired version; in this case, Python 3.12:
PS \\Users\[user]> python
Python 3.12.2 (tags/v3.12.2:6abddd9, Feb 6 2024, 21:26:36)
[MSC v.1937 64 bit (AMD64)] on win32
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>>
If you are using macOS, you may change the PATH environment variable by simply setting an alias in your shell profile files (such as ~/.bashrc or ~/.zshrc) by adding the line:
alias python='python3.12'
Or, you may follow the following steps to modify the $PATH environment variable:
Check Python installation and the default Python version. (The example below shows that Python3 and Python 3.12 are recognized by the system.)
[user]@mac:~$ which python
[user]@mac:~$ which python3
/opt/homebrew/bin/python3
[user]@mac:~$ which python3.12
/opt/homebrew/bin/python3.12
[user]@mac:~$
Edit shell configuration (~/.bashrc or ~/.zshrc)
nano ~/.zshrc ### if using zsh
nano ~/.bashrc ### if using bash
Add preferred Python (system-installed) version to PATH to
.bashrcor.zshrc
export PATH="/usr/local/bin/python3.12:$PATH"
or, if installed via Homebrew:
export PATH="/opt/homebrew/bin:$PATH"
Apply changes by exiting and restarting the terminal, or:
source ~/.zshrc ### if using zsh
source ~/.bashrc ### if using bash

