19. Machine Learning#
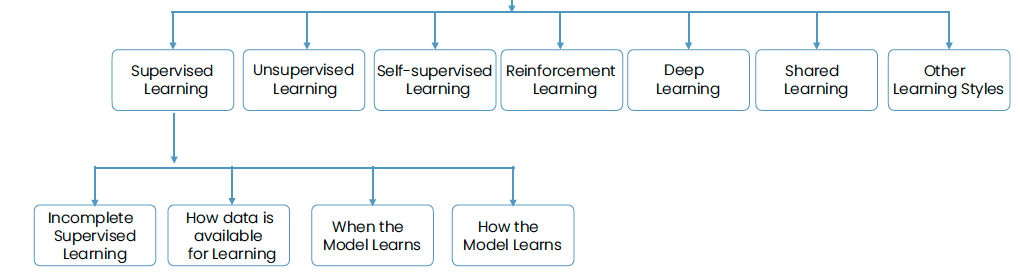
Fig. 19.1 Types of Machine Learning#
Algorithm Family
What are these? Make table and add description
Regression
Classification
Ranking
Clustering
Pattern detection
Time Series
Anomaly detection
Survival analysis
Causal analysis
Ref.: Vidya (2025), p.66
Model Validation
Training dataset validation
Validation dataset validation (optional)
Test dataset validation
Model Evaluation Goals
Regression
• The primary goal is Predictive Accuracy, which assesses how accurately the regression model predicts continuous target values, ensuring that the predicted values closely match the actual values.
Residual Analysis analyzes and minimizes the residuals (the differences between predicted and actual values) to ensure that the model captures underlying patterns in the data.
Classification
Evaluate Discriminative Power, the model’s ability to discriminate between different classes by assessing metrics like accuracy or precision-recall curves. Address class imbalance issues to achieve a balanced classification performance, especially in scenarios with imbalanced class distributions.
Ranking
Relevance Ranking assesses how well the model ranks items or documents by their relevance to a user query or context.
Rank Stability ensures the stability of rankings across different queries or situations, indicating the reliability of the ranking model.
Clustering
For Clustering problems, Cluster Purity is an indicator of how similar the data points in the same cluster are and how different data points in other clusters are, aiming for high cluster purity.
Evaluate the interpretability of the clusters and whether they align with domain knowledge or expectations.
Pattern detection
In Pattern Mining, we assess the model’s ability to discover meaningful patterns, associations, or trends within data, ensuring it captures relevant information.
Generalization evaluates how well the model generalizes patterns to new or unseen data, avoiding overfitting.
Time Series
For problems that involve Time series, Forecasting Accuracy evaluates the accuracy of time series forecasting models in predicting future values using metrics like Mean Absolute Error (MAE) or Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE).
Seasonal Decomposition assesses the ability to capture and interpret seasonal patterns, trends, and noise within time series data.
Anomaly detection
Anomaly Detection Rate measures the ability to identify anomalies effectively while minimizing false positives, often using metrics like precision and recall.
Threshold Tuning optimizes the anomaly detection threshold to balance sensitivity and specificity per the specific application’s requirements.
Survival analysis
Causal analysis
Ref.: Vidya (2025), p.68-69
How Much Data for ML Models?
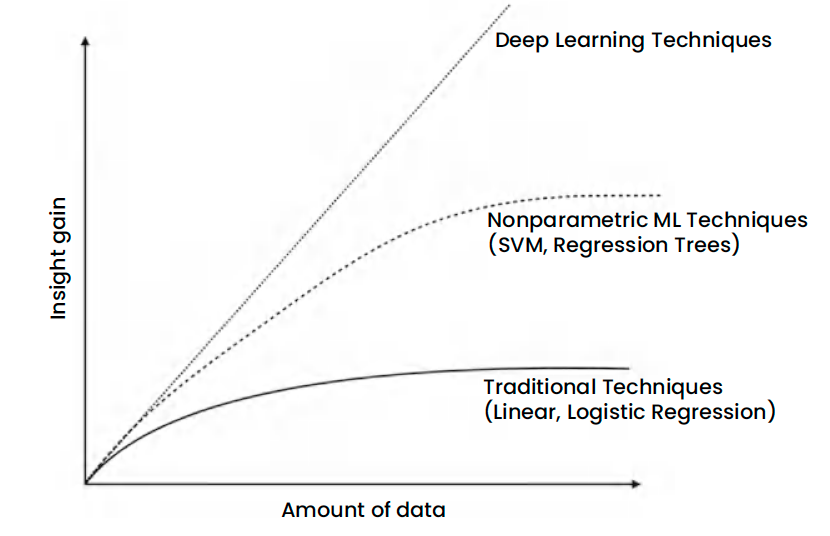
Fig. 19.2 Data Needed for an ML Model (Vidya, 2025, pp.71)#
Data Types

Fig. 19.3 Amount of Data Needed for an ML Model (Vidya, 2025, pp.71)#
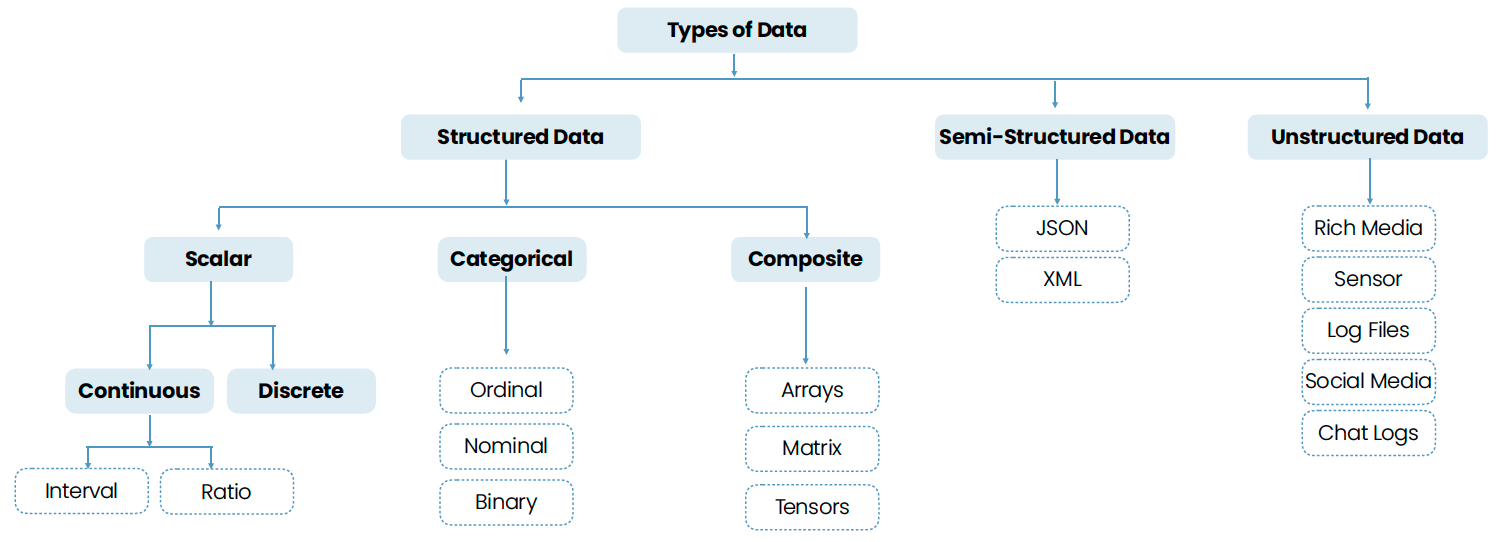
Fig. 19.4 Type of Data in Data Science (Vidya, 2025, pp.71)#
